Improvement and Integration of People Management System
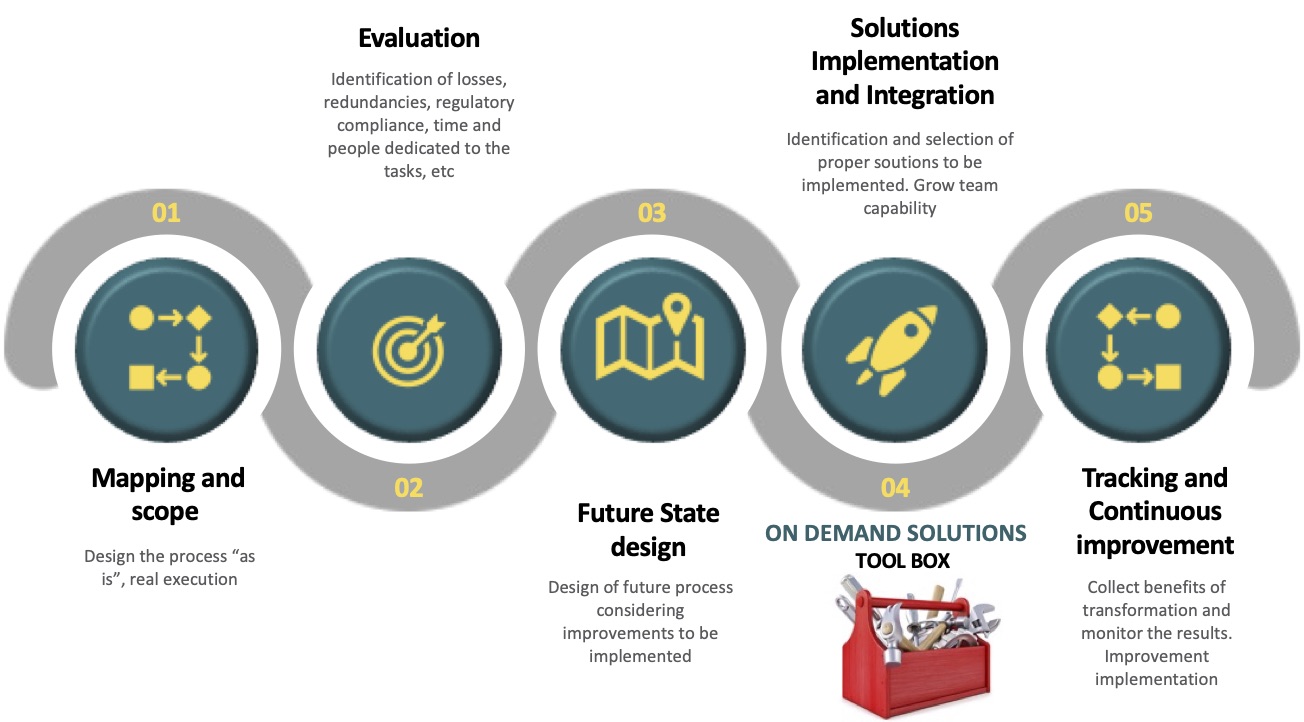
The phase of process assessment is a critical component of evaluating and improving various organizational processes. It typically involves the following key steps:
- Identifying the Process: The first step in process assessment is to clearly define and identify the specific process that needs to be assessed. This includes understanding its purpose, objectives, and the various stakeholders involved.
- Gathering Data: During this phase, data related to the process is collected. This data can come from various sources, including process documentation, interviews with employees, analysis of historical performance data, and observation of how the process is currently executed.
- Process Mapping: Creating a visual representation of the process, often in the form of flowcharts or diagrams, is a common practice in process assessment. This helps in understanding the sequence of activities, decision points, and interactions within the process.
- Performance Metrics: Identifying and defining key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of the process. These metrics should align with the process objectives and can include measures like cycle time, cost, quality, and efficiency.
- Analysis and Evaluation: This step involves a thorough examination of the collected data and the process map. It aims to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, deviations from standards, and areas for improvement. Benchmarking against industry best practices can also be part of the assessment.
- Stakeholder Feedback: Involving stakeholders who are directly or indirectly affected by the process is crucial. Collecting their feedback, concerns, and suggestions can provide valuable insights into the process’s strengths and weaknesses.
- Risk Assessment: Assessing the risks associated with the process is important. This involves identifying potential areas where errors, delays, or compliance issues may arise.
- Compliance and Legal Considerations: Ensuring that the process complies with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards is essential. This can involve a legal or compliance review.
- Documenting Findings: The results of the assessment are documented in a clear and concise report. This report will summarize the current state of the process, identify areas for improvement, and provide recommendations for enhancing the process.
- Future State – Action Plan: An action plan is developed to address the identified issues and opportunities for improvement. It outlines specific steps, responsibilities, timelines, and resources required to make necessary changes.
- Solutions Implementation & Automatization: Once the action plan is approved, the process improvements are implemented and automatized. This may involve training, reengineering, software upgrades, or other changes to the process.
- Monitoring and Continuous Improvement: After implementing changes, ongoing monitoring and measurement of the process performance are essential. Feedback from stakeholders and further adjustments are made as necessary to ensure sustained improvement.
The methodology is a systematic approach to understanding, analyzing, and optimizing HR processes, leading to increased efficiency, effectiveness, and alignment with organizational goals and standards. It is often an interative process, as organizations continually strive to enhance their operations.
